Comprehensive Guide to the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
Introduction to the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
Understanding your vehicle’s transmission system is crucial for both seasoned mechanics and enthusiastic car owners. The ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram, although complex, is a valuable resource for grasping how your car’s transmission operates. This diagram provides insights into the operation of solenoids, which are integral to the automatic transmission system. By familiarizing yourself with this diagram, you can enhance your knowledge and maintain optimal driving performance.
The Role of Solenoids in Transmission Systems
Solenoids are vital components in automatic transmissions, responsible for controlling various functions such as gear shifts and fluid flow. They ensure that your vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently. Delving into the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram can help you understand how these components work together, preparing you for potential issues and enhancing your ability to troubleshoot and repair transmission problems.
Understanding the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
Overview of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 is a six-speed automatic transmission developed by ZF Friedrichshafen AG, a prominent German manufacturer. Renowned for its durability and efficiency, this transmission is widely used in high-performance vehicles from brands such as BMW, Audi, and Jaguar. The Generation 2 model builds on the first-generation 6HP, offering improved fuel efficiency, quicker shifting, and enhanced overall performance.
Importance of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission is celebrated for its smooth shifting and robust performance. This advanced transmission system relies on a network of solenoids within the valve body to regulate fluid pressure, engage clutches, and achieve desired gear changes. Understanding the solenoid diagram is crucial for anyone involved in repairing or maintaining this transmission, as it provides essential information for accurate diagnosis and repair.
Key Components of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
Solenoids and Their Functions
In the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission, solenoids act as electronically controlled valves that manage fluid pressure within the system. These solenoids play a critical role in controlling gear shifts and ensuring smooth operation. By referring to the solenoid diagram, technicians can identify and understand the function of each solenoid, facilitating effective troubleshooting and repair.
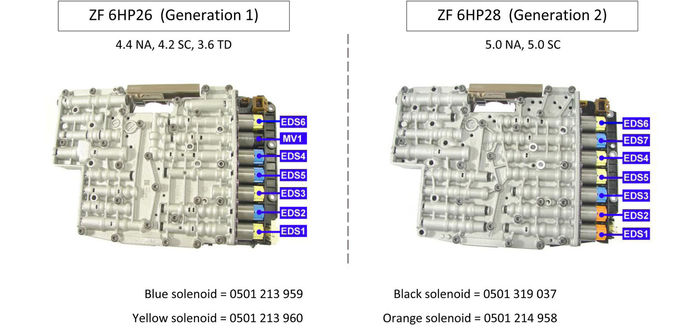
Enhancements in the Generation 2 Transmission
The Generation 2 version of the ZF 6HP transmission incorporates several enhancements over its predecessor. These improvements include better efficiency, faster shifting times, and increased reliability. The solenoid diagram for the Generation 2 transmission reflects these upgrades, providing a detailed view of the enhanced solenoid system.
Practical Applications of the Solenoid Diagram
For automotive professionals and enthusiasts, the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram is an indispensable tool. It helps in diagnosing issues, performing maintenance, and ensuring that the transmission operates as intended. By understanding the diagram, one can gain insights into the system’s functionality and address any problems that may arise.
Understanding the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
Identifying Key Solenoids in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Diagram
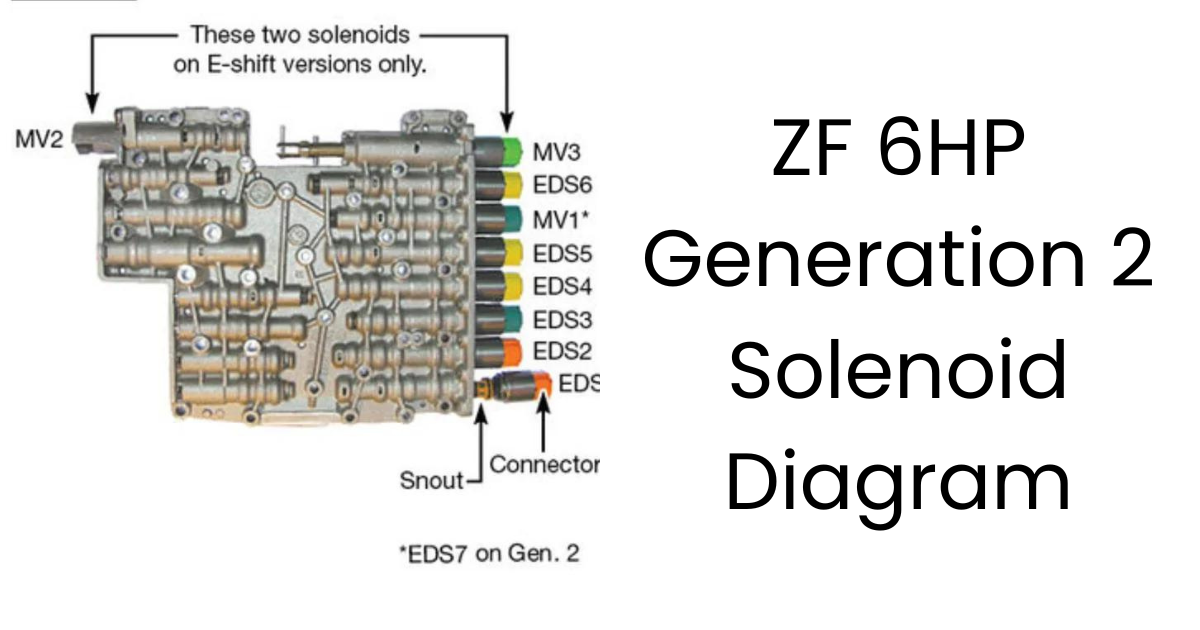
To effectively work with the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission, it is essential to understand the different solenoids depicted in the solenoid diagram. Here’s a detailed overview of the common solenoids you’ll encounter:
Pressure Control Solenoids (EDS)
Pressure control solenoids, often labeled EDS, are crucial for regulating the overall line pressure within the transmission. These solenoids, typically numbered EDS 1, EDS 2, etc., each control specific pressure zones to ensure optimal operation.
Shift Solenoids (SL)
Shift solenoids manage the engagement of specific clutches by directing hydraulic pressure. For instance, the SL1 solenoid controls the A/C clutch, while the SL2 solenoid is responsible for the B clutch. These solenoids are essential for smooth gear transitions.
Torque Converter Lockup (TCC) Solenoid
The TCC solenoid handles the engagement of the torque converter clutch, which enhances fuel efficiency, especially during steady cruising conditions. This solenoid plays a key role in optimizing the vehicle’s performance.
Manual Valve (MV)
Often referred to as the EPC (Electronic Pressure Control) solenoid, the manual valve regulates the pressure supplied to the shift solenoids. This, in turn, affects the characteristics of gear changes. Understanding its function is important for diagnosing shifting issues.
Keep in mind that the arrangement and naming of solenoids might vary slightly depending on the specific vehicle application. Always consult the appropriate ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram or service manual for the most accurate information.
Key Features of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
Improvements in the Generation 2 Transmission
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission offers several upgrades compared to its predecessor. Notable enhancements include:
- Faster Shift Times: The second-generation model provides quicker gear changes, improving overall driving performance.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: With better design and control mechanisms, this transmission contributes to greater fuel economy.
- Increased Torque Capacity: The upgraded system can handle higher torque, making it suitable for more demanding driving conditions.
Additionally, the Generation 2 transmission features advanced electronic controls and a refined hydraulic system, resulting in smoother and more precise gear shifts. These improvements make it a favored choice in modern high-performance vehicles.
Components and Their Functions in the Solenoid Diagram
Essential Components in the Solenoid Diagram
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram highlights several key components, each integral to the transmission’s functionality:
Solenoids
Solenoids are electromagnetic devices that control fluid flow by opening and closing valves according to electrical signals from the control unit. They are fundamental to regulating the transmission’s hydraulic system.
Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors monitor hydraulic pressure levels within the transmission. They provide critical feedback to ensure proper shifting and help maintain optimal performance.
Valve Body
The valve body is a complex component that contains multiple passages and valves. It directs hydraulic fluid to various parts of the transmission, facilitating gear engagement and proper function.
Connectors
Connectors link the various components, ensuring effective communication between the electronic controls and mechanical parts. Reliable connections are crucial for the smooth operation of the transmission system.
Understanding these components and how they interact will help you diagnose and resolve issues more effectively, ensuring the transmission operates efficiently.
Exploring the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
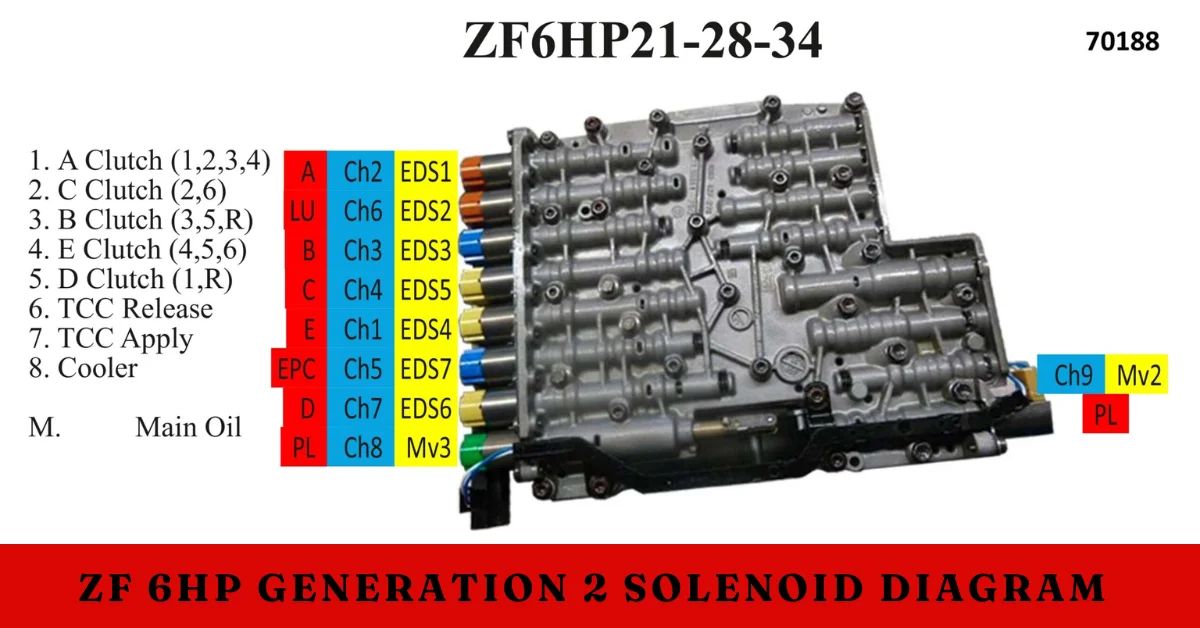
The solenoid diagram for the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission provides a comprehensive visual layout of the solenoid system and its various components. Understanding this diagram is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. Here’s an overview of the key elements typically depicted in the diagram:
Solenoid Placement
The diagram indicates the specific locations of each solenoid within the transmission assembly. This information is critical for technicians, as it helps locate and access solenoids that may require service or replacement.
Hydraulic Fluid Pathways
Illustrated within the diagram are the pathways through which hydraulic fluid circulates in the transmission. The diagram shows how fluid flows through different valves and channels, regulated by the solenoids, to effectuate gear changes.
Electrical Connections
Included in the diagram are the electrical connections between the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the solenoids. It details the wiring and connectors that transmit signals from the ECU to the solenoids, ensuring proper operation.
Solenoid Functions
The diagram labels each solenoid’s function, specifying which solenoid manages which gear or pressure circuit. This information is crucial for understanding the transmission’s operation and for diagnosing potential issues.
Notable Features of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
Six-Speed Gear System
This transmission features a six-speed gear setup, providing a broad range of gear ratios. This design enhances both performance and fuel efficiency.
Adaptive Shift Logic
The adaptive shift logic adjusts gear-changing patterns based on driving conditions and driver behavior, optimizing the transmission’s performance in various scenarios.
Torque Converter with Lock-Up Clutch
The transmission includes a torque converter with a lock-up clutch, which boosts fuel efficiency and offers smoother acceleration.
Advanced Hydraulic Control System
The system utilizes sophisticated solenoids to regulate fluid flow and pressure, leading to improved control and efficiency in gear shifting.
Interpreting the Solenoid Diagram
When examining the solenoid diagram, it is important to recognize the following symbols and notations:
Solenoid Symbols
Solenoids are typically represented by small boxes or circles, each labeled with an identifier (e.g., Solenoid A, Solenoid B). These symbols denote the specific solenoids within the system.
Fluid Pathways
Fluid pathways are shown as lines connecting solenoids to various components of the transmission. These lines illustrate the flow of hydraulic fluid through the system.
Electrical Connections
Electrical connections are depicted as lines or arrows linking solenoids to the ECU or other electrical components, indicating how signals are transmitted.
Common Solenoid-Related Issues in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmission
Solenoids, being electronic components, can experience wear and eventual failure. Here are some typical issues associated with malfunctioning solenoids:
Shifting Problems
Erratic gear shifts, delayed engagements, or slipping between gears may indicate a malfunctioning shift solenoid. These issues can disrupt smooth gear transitions.
Pressure Control Issues
A failing pressure control solenoid can result in inadequate or excessive line pressure, leading to harsh shifts or a lack of power transfer. Proper pressure regulation is crucial for smooth operation.
Torque Converter Vibrations
Problems with the torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid may cause noticeable vibrations during the torque converter lock-up phase. This issue can affect driving comfort and performance.
Understanding these components and their functions helps in diagnosing and addressing transmission issues effectively, ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
Importance of Using High-Quality Parts and Following Proper Procedures
The Role of Quality Parts in Transmission Maintenance
Utilizing high-quality replacement solenoids is crucial for maintaining the health of your transmission. Inferior parts can lead to premature failures and exacerbate transmission problems. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for disassembly and reassembly is equally important to ensure correct operation and avoid leaks or mechanical failures.
Recommended Resources for ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Information
To gain a deeper understanding of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram and valve body functionality, consider these resources:
ZF Technical Documentation
ZF provides specialized documentation and repair manuals for their transmissions. Although some information may require a paid subscription, these resources are invaluable for professional mechanics seeking detailed technical insights.
Transmission Parts Suppliers
Reputable transmission parts suppliers offer detailed catalogs with information on solenoids compatible with the ZF 6HP Generation 2. These catalogs often include technical specifications and guidelines for solenoid replacement.
Online Repair Forums
Online forums frequented by experienced transmission technicians can be a valuable source of knowledge and troubleshooting advice. Engaging with these communities can provide practical insights and tips related to ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmissions.
Common Issues with ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoids
Symptoms of Malfunctioning Solenoids
Faulty solenoids can significantly impact transmission performance, presenting in various ways. Common signs of solenoid issues include:
- Delayed or Rough Gear Shifts: Gear changes may become sluggish or harsh.
- Transmission Slippage: The vehicle may exhibit unexpected slipping between gears.
- Unplanned Downshifts: Sudden downshifts may occur without driver input.
- Limp Mode Activation: The transmission may default to a single gear to avoid further damage.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help mitigate more severe transmission problems.
Causes of Solenoid Failure
Several factors can lead to solenoid failure in the ZF 6HP transmission:
- Wear and Tear: Regular use can wear out solenoids over time.
- Contaminated Transmission Fluid: Contaminants in the fluid can affect solenoid performance.
- Electrical Issues: Short circuits or damaged wiring can disrupt solenoid function.
Understanding these causes can assist in preventive maintenance and prolong the transmission’s lifespan.
Diagnosing Solenoid Issues
Diagnosing solenoid problems involves:
- Visual Inspections: Look for damaged wiring or loose connections.
- Electrical Testing: Use specialized tools to check solenoid continuity and resistance, ensuring they fall within the specified range.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Reading DTCs can provide insights into solenoid performance.
Troubleshooting Tips for Solenoid Problems
When addressing issues with the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram:
- Conduct a Visual Inspection: Examine for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Measure Solenoid Resistance: Utilize a multimeter to check resistance levels. Readings outside the recommended range may indicate a problem.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: Uncommon sounds, such as clicking or grinding, can indicate internal issues.
- Check Transmission Fluid: Ensure fluid levels are adequate and the fluid is not contaminated, as this can affect solenoid operation.
If problems persist, refer to specific service manuals for detailed diagnostic procedures tailored to your vehicle. For complex issues, seeking professional help may be necessary, as some problems require expert intervention.
Conclusion
The solenoid system in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission is vital for ensuring smooth and efficient operation. A thorough understanding of the solenoid diagram is essential for anyone involved in the maintenance, repair, or study of this advanced transmission system. The diagram provides a detailed visual representation of solenoids, hydraulic pathways, and electrical connections, which is invaluable for troubleshooting, maintenance, and education. This knowledge helps ensure that the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission continues to perform at its best across a wide range of vehicles.
By gaining insight into the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram, you acquire a critical perspective on the internal workings of this modern transmission. This understanding empowers you to diagnose potential solenoid-related issues and undertake basic troubleshooting. For more complex repairs, including disassembly and reassembly of the valve body, consulting a certified transmission specialist is highly recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions about ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoids
How Long Do ZF 6HP Solenoids Typically Last?
The longevity of ZF 6HP solenoids can vary depending on driving conditions, maintenance practices, and the overall health of the transmission. Generally, solenoids can last between 100,000 and 150,000 miles. Regular maintenance, such as timely transmission fluid changes, can help extend their lifespan and maintain reliable performance.
Can Solenoids Be Repaired or Only Replaced?
In most instances, solenoids are replaced rather than repaired. While minor issues like electrical connection problems may be addressed, internal failures typically necessitate replacement. Utilizing high-quality replacement solenoids and adhering to proper installation procedures can restore the transmission’s performance and reliability.
What Are the Costs Involved in Solenoid Replacement?
The cost of replacing solenoids can vary based on factors such as the specific solenoids being replaced, labor charges, and the vehicle’s make and model. On average, solenoid replacement costs range from $200 to $500 per solenoid, including labor. To manage costs effectively, consider obtaining quotes from multiple repair shops and using OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts.